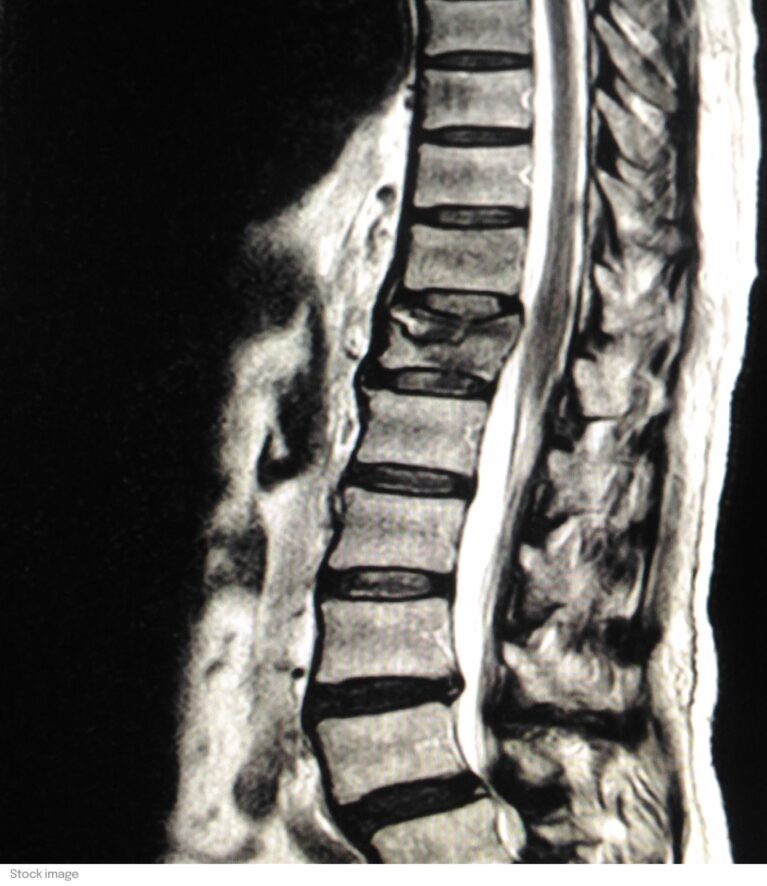
Spinal fracture
There are several types of spinal fracture:
- High kinetic fractures on healthy bone, after a major trauma or at high speed (car accident, fall from a height, etc.).
- Fractures on pathological bone, after a minor shock, such as a fall while standing or walking, or carrying a heavy load. The bone is weakened, usually due to osteoporosis caused by age or medical treatments. The bone can also be weakened by metastases that have settled in the vertebral body.
The most obvious symptom of a fracture is pain localized to the affected vertebra. The diagnosis is made with the help of medical imaging (X-ray, scanner or MRI).
Treatment initially consists of prescribing painkillers. The patient may be immobilized with a brace to allow the bone to heal. If the pain persists, the fracture may be consolidated by injecting cement (vertebroplasty), sometimes combined with a straightening of the vertebra (kyphoplasty) to restore its height and/or strength. Posterior arthrodesis may also be proposed to fuse the vertebrae and relieve pain.